 Roche - Understanding the impact of bladder cancer
Roche - Understanding the impact of bladder cancerHow do you get vegetable seeds? Question date: 2006-06-05 Answer 1:Thank you for sending this important question. I hope my answer will help you understand a very important difference between fruits and fruits vegetables you can pass to your friends and classmates (and even some adults). As you know, plants have many different parts, so let's start by listing some of the them. The parts that are buried under soil - roots - help plants take food and water from the ground. The long, thin part that grows above the ground and supports the the rest of the plant is called stem. Sheets grow around the stem uses sunlight to make food for the rest of the plant. You've probably noticed. during certain times of the year, flowers bloom and eventually become fruits. Inside fruits are seeds. If the fruits are not chosen and sent to your favorite supermarket, He'll eventually fall to the ground. In time, small microscopic creatures, insects and some small animals will eat the fleshy part of the fruit that surrounds the seeds. The seed that is leaving behind will finally grow to become a new plant. Simple, right? Well, not exactly. You'd be surprised to hear those botanists. .. scientists who study plants of all kinds -- Call anything with seeds inside a "fruit"! This means tomatoes, peas podes, cucumbers, peppers, pumpkin and avocados are all fruits, even Even though many people call them vegetables! Why? You guessed because everyone has seeds. inside. If you don't believe me, ask an adult. to cut them off so you can see yourself. According to the botanists, really. they take vegetables from different parts of plants that have no seeds, like leaves, stems and roots. Spinach and cabbage are really the leaves of certain plants. Asparagus and The celery is stems. Cartoons, radishes, paddles and trousers Nabos (yuk) are roots. What do you have all in Whole? No seeds! So all these parts of the plant are Real vegetables So, after all I have Do you think you'd be so The success of taking vegetable seeds? From Of course not because they have nothing! You. I shouldn't feel bad if you didn't know... many Answer 2:Most vegetables (e.g. bean pods, pumpkins, etc.) tomatoes) are the non-sweet fruits of flowering plants, which means they have seeds in them because they evolved as planting structures. Normally, a fruit "without seeds" is a fruit that has modified to make the seeds soft and can be bit easily (for example, a seedless watermelon), or have seeds not (I can't think of a good example). But... such vegetables have seeds. Vegetables than are not fruits (e.g. broccoli, asparagus) Have seeds. Click to return to the search form. Copyright © 2020 Los Regentes de la Universidad de California, All rights reserved. How do you get vegetable seeds? Question date: 2006-06-05 Answer 1:Thank you for sending this important question. I hope my answer will help you understand a very important difference between fruits and fruits vegetables you can pass to your friends and classmates (and even some adults). As you know, plants have many different parts, so let's start by listing some of the them. The parts that are buried under soil - roots - help plants take food and water from the ground. The long, thin part that grows above the ground and supports the the rest of the plant is called stem. Sheets grow around the stem uses sunlight to make food for the rest of the plant. You've probably noticed. during certain times of the year, flowers bloom and eventually become fruits. Inside fruits are seeds. If the fruits are not chosen and sent to your favorite supermarket, He'll eventually fall to the ground. In time, small microscopic creatures, insects and some small animals will eat the fleshy part of the fruit that surrounds the seeds. The seed that is leaving behind will finally grow to become a new plant. Simple, right? Well, not exactly. You'd be surprised to hear those botanists. .. scientists who study plants of all kinds -- Call anything with seeds inside a "fruit"! This means tomatoes, peas podes, cucumbers, peppers, pumpkin and avocados are all fruits, even Even though many people call them vegetables! Why? You guessed because everyone has seeds. inside. If you don't believe me, ask an adult. to cut them off so you can see yourself. According to the botanists, really. they take vegetables from different parts of plants that have no seeds, like leaves, stems and roots. Spinach and cabbage are really the leaves of certain plants. Asparagus and The celery is stems. Cartoons, radishes, paddles and trousers Nabos (yuk) are roots. What do you have all in Whole? No seeds! So all these parts of the plant are Real vegetables So, after all I have Do you think you'd be so The success of taking vegetable seeds? From Of course not because they have nothing! You. I shouldn't feel bad if you didn't know... many Answer 2:Most vegetables (e.g. bean pods, pumpkins, etc.) tomatoes) are the non-sweet fruits of flowering plants, which means they have seeds in them because they evolved as planting structures. Normally, a fruit "without seeds" is a fruit that has modified to make the seeds soft and can be bit easily (for example, a seedless watermelon), or have seeds not (I can't think of a good example). But... such vegetables have seeds. Vegetables than are not fruits (e.g. broccoli, asparagus) Have seeds. Click to return to the search form. Copyright © 2020 Los Regentes de la Universidad de California, All rights reserved. How do you get vegetable seeds? Question date: 2006-06-05 Answer 1:Thank you for sending this important question. I hope my answer will help you understand a very important difference between fruits and fruits vegetables you can pass to your friends and classmates (and even some adults). As you know, plants have many different parts, so let's start by listing some of the them. The parts that are buried under soil - roots - help plants take food and water from the ground. The long, thin part that grows above the ground and supports the the rest of the plant is called stem. Sheets grow around the stem uses sunlight to make food for the rest of the plant. You've probably noticed. during certain times of the year, flowers bloom and eventually become fruits. Inside fruits are seeds. If the fruits are not chosen and sent to your favorite supermarket, He'll eventually fall to the ground. In time, small microscopic creatures, insects and some small animals will eat the fleshy part of the fruit that surrounds the seeds. The seed that is leaving behind will finally grow to become a new plant. Simple, right? Well, not exactly. You'd be surprised to hear those botanists. .. scientists who study plants of all kinds -- Call anything with seeds inside a "fruit"! This means tomatoes, peas podes, cucumbers, peppers, pumpkin and avocados are all fruits, even Even though many people call them vegetables! Why? You guessed because everyone has seeds. inside. If you don't believe me, ask an adult. to cut them off so you can see yourself. According to the botanists, really. they take vegetables from different parts of plants that have no seeds, like leaves, stems and roots. Spinach and cabbage are really the leaves of certain plants. Asparagus and The celery is stems. Cartoons, radishes, paddles and trousers Nabos (yuk) are roots. What do you have all in Whole? No seeds! So all these parts of the plant are Real vegetables So, after all I have Do you think you'd be so The success of taking vegetable seeds? From Of course not because they have nothing! You. I shouldn't feel bad if you didn't know... many Answer 2:Most vegetables (e.g. bean pods, pumpkins, etc.) tomatoes) are the non-sweet fruits of flowering plants, which means they have seeds in them because they evolved as planting structures. Normally, a fruit "without seeds" is a fruit that has modified to make the seeds soft and can be bit easily (for example, a seedless watermelon), or have seeds not (I can't think of a good example). But... such vegetables have seeds. Vegetables than are not fruits (e.g. broccoli, asparagus) Have seeds. Click to return to the search form. How do you get vegetable seeds? Answer 1:Thank you for sending this important question. I hope my answer will help you understand a very important difference between fruits and fruits vegetables you can pass to your friends and classmates (and even some adults). As you know, plants have many different parts, so let's start by listing some of the them. The parts that are buried under soil - roots - help plants take food and water from the ground. The long, thin part that grows above the ground and supports the the rest of the plant is called stem. Sheets grow around the stem uses sunlight to make food for the rest of the plant. You've probably noticed. during certain times of the year, flowers bloom and eventually become fruits. Inside fruits are seeds. If the fruits are not chosen and sent to your favorite supermarket, He'll eventually fall to the ground. In time, small microscopic creatures, insects and some small animals will eat the fleshy part of the fruit that surrounds the seeds. The seed that is leaving behind will finally grow to become a new plant. Simple, right? Well, not exactly. You'd be surprised to hear those botanists. .. scientists who study plants of all kinds -- Call anything with seeds inside a "fruit"! This means tomatoes, peas podes, cucumbers, peppers, pumpkin and avocados are all fruits, even Even though many people call them vegetables! Why? You guessed because everyone has seeds. inside. If you don't believe me, ask an adult. to cut them off so you can see yourself. According to the botanists, really. they take vegetables from different parts of plants that have no seeds, like leaves, stems and roots. Spinach and cabbage are really the leaves of certain plants. Asparagus and The celery is stems. Cartoons, radishes, paddles and trousers Nabos (yuk) are roots. What do you have all in Whole? No seeds! So all these parts of the plant are Real vegetables So, after all I have Do you think you'd be so The success of taking vegetable seeds? From Of course not because they have nothing! You. I shouldn't feel bad if you didn't know... many Answer 2:Most vegetables (e.g. bean pods, pumpkins, etc.) tomatoes) are the non-sweet fruits of flowering plants, which means they have seeds in them because they evolved as planting structures. Normally, a fruit "without seeds" is a fruit that has modified to make the seeds soft and can be bit easily (for example, a seedless watermelon), or have seeds not (I can't think of a good example). But... such vegetables have seeds. Vegetables than are not fruits (e.g. broccoli, asparagus) Have seeds. Copyright © 2020 Los Regentes de la Universidad de California, All rights reserved.
What is the difference between a fruit and a vegetable? For 12 June 2012 A peach is a fruit, whoever you are, and a carrot is definitely a vegetable. But in the Venn diagram that links these two product categories, there is a region of overlap. It results from the fact that "fruit" and "vegetable" are defined differently depending on whether you are a gardener or a chef. The dead center of the superimposed region is . Then why is it a fruit, and why is it a vegetable? Botanically speaking, a fruit is a plant structure that develops from the ovary of a flowering plant, while the vegetables are all other parts of the plant, such as roots, leaves and stems. By those standards, the growths of the vediac like , the escamos and, yes, the tomatoes are all fruits, while the roots like the beets, and the wolves, leaves like , and lettuce, and stems like and are all the vegetables. Related: The panorama is very different in culinary terms, however. Many foods that are (botanically speaking) fruits, but which are salted instead of sweets, are typically considered vegetables by chefs. This includes botanical fruits such as eggplants, bell peppers and tomatoes. The debate of fruits vs. vegetables can sometimes reach such a fever field that the law should enter. In the Nix case. c. Hedden of 1893 of the Supreme Court of the United States, the court unanimously ruled that an imported tomato should be imposed as a vegetable, instead of as a fruit (without taxes). The court recognized that a tomato is a botanical fruit, but it was with what they called the "ordinary" definitions of fruits and vegetables, those used in the kitchen. Original article on Life Sciences. Stay up to date on the coronavirus outbreak when you sign up for our newsletter today. Thanks for signing up for Live Science. You will receive a verification email shortly. There was a problem. Please refresh the page and try again. Live Science is part of Future US Inc, an international media group and a leading digital editor. . Future US, Inc. 11 West 42nd Street, 15th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
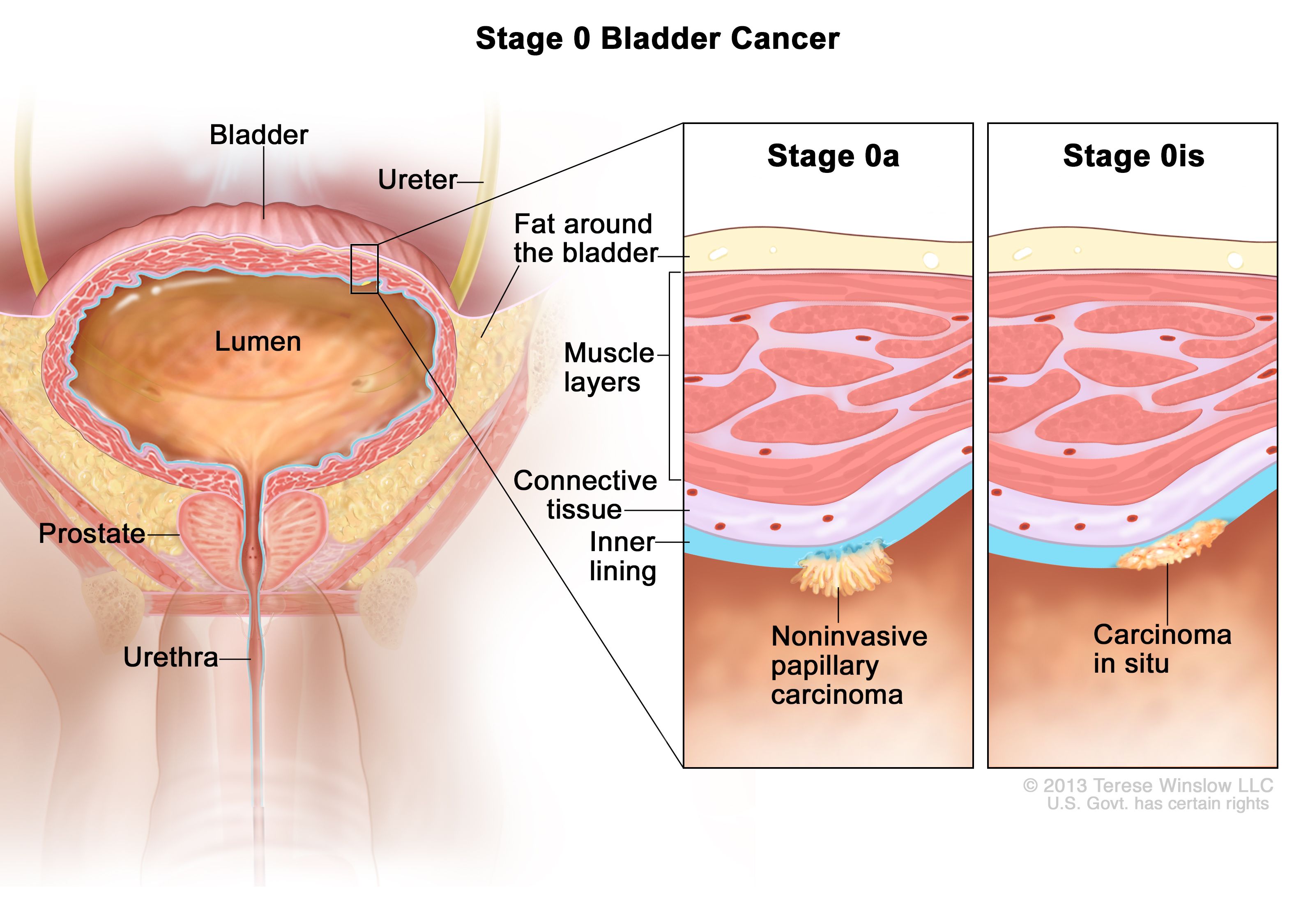
Bladder Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version - National Cancer Institute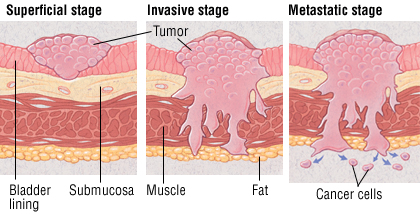
Bladder Cancer - Harvard Health
Bladder Cancer Survival after Surgery
Bladder cancer survival statistics | Cancer Research UK
Survival Rate - Urinary Bladder Cancer The Hidden Menace
Stage 2 Bladder Cancer: Outlook, Treatment, and More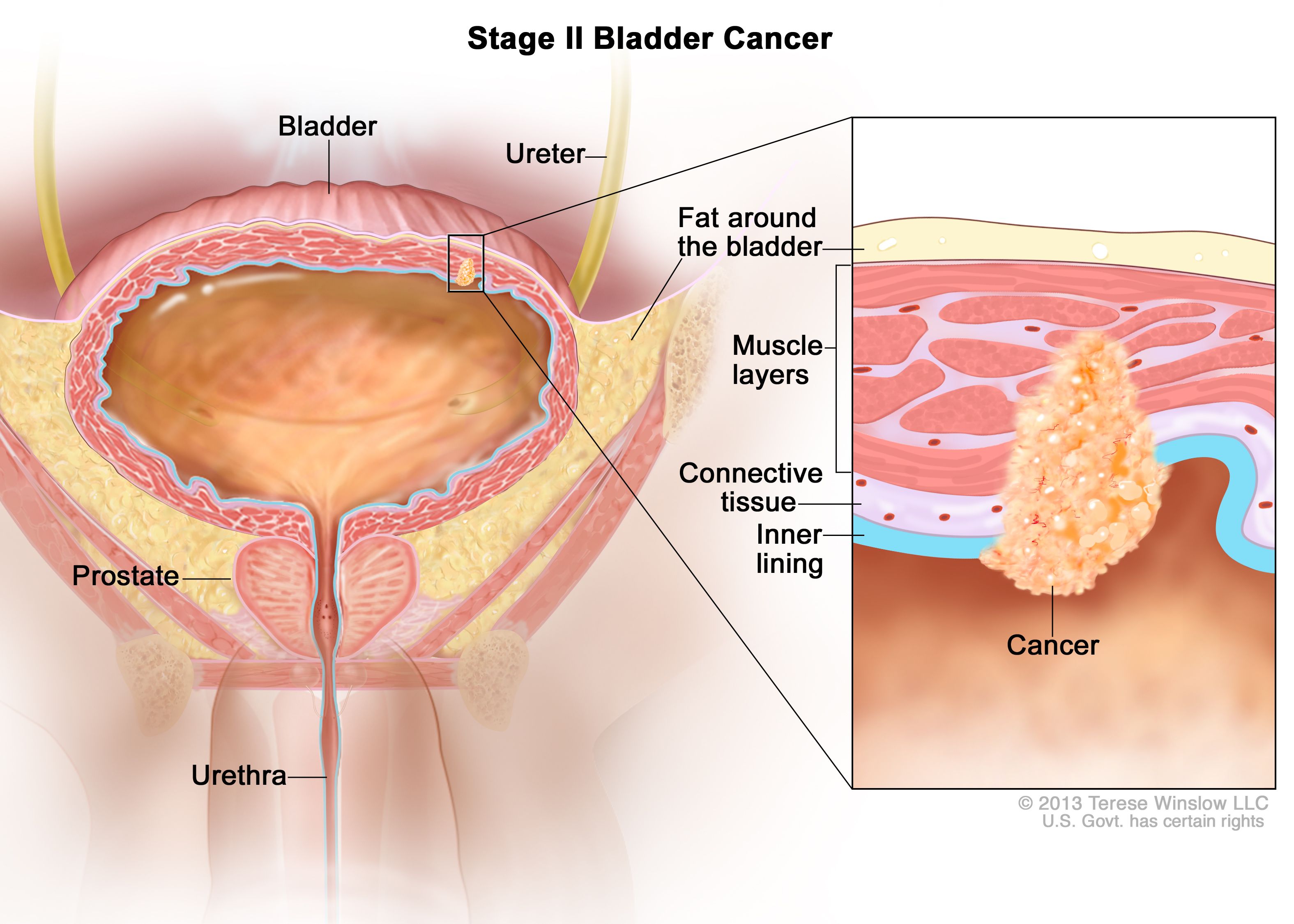
Bladder Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)–Patient Version - National Cancer Institute
Bladder Cancer Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
NSAUA 2018: The Curability of Invasive Bladder Cancer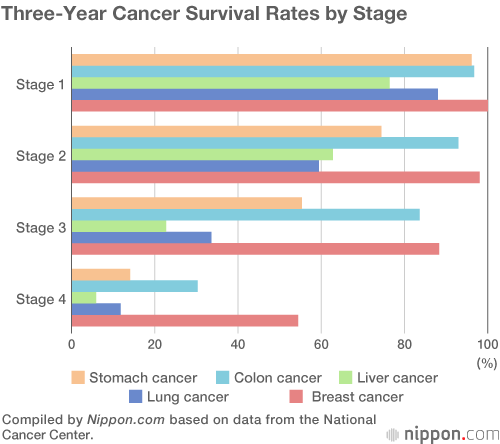
Beating the Big C: Three-Year Cancer Survival Rate at 71% | Nippon.com
Kaplan–Meier overall survival analysis for bladder cancer patients in... | Download Scientific Diagram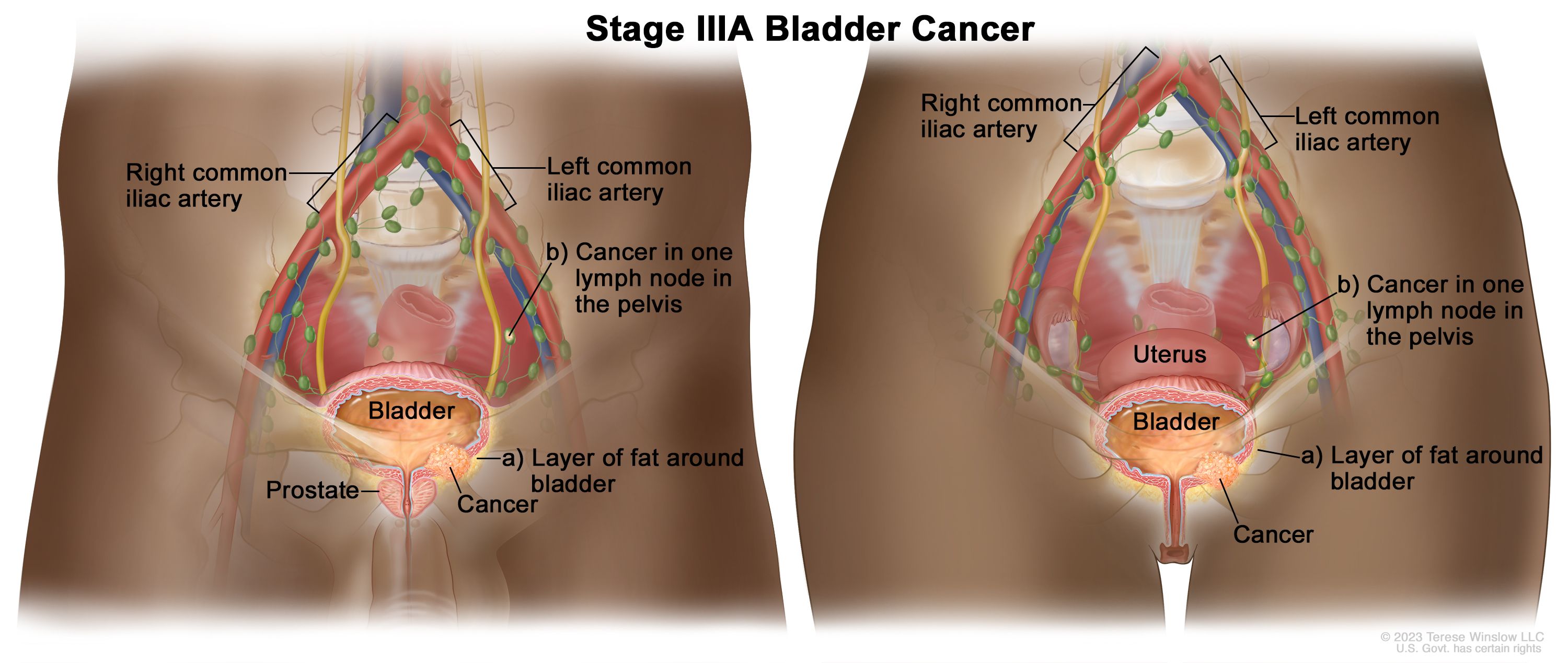
Bladder Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)–Patient Version - National Cancer Institute
Bladder Cancer Symptoms Pictures: Warning Signs, Treatments, Survival Rates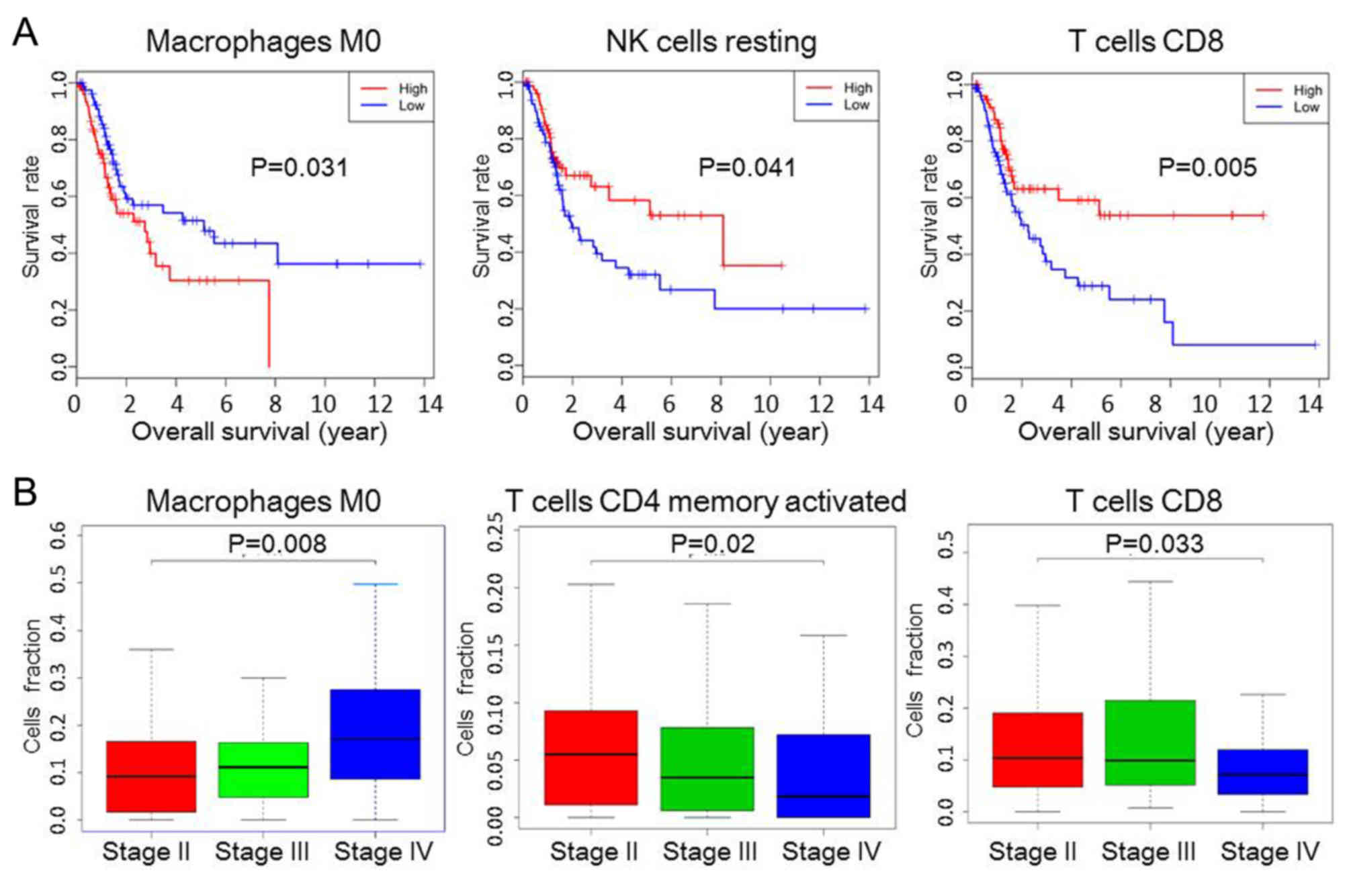
Prognostic value of immune cell infiltration in bladder cancer: A gene expression‑based study
Increased Proliferation as Independent Predictor of Disease Recurrence in Initial Stage pTa Urothelial Bladder Cancer - IOS Press
Staging and grading of bladder cancer - Macmillan Cancer Support
Delaying Radical Cystectomy After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer is Associated with Adverse Survival Outcomes - European Urology Oncology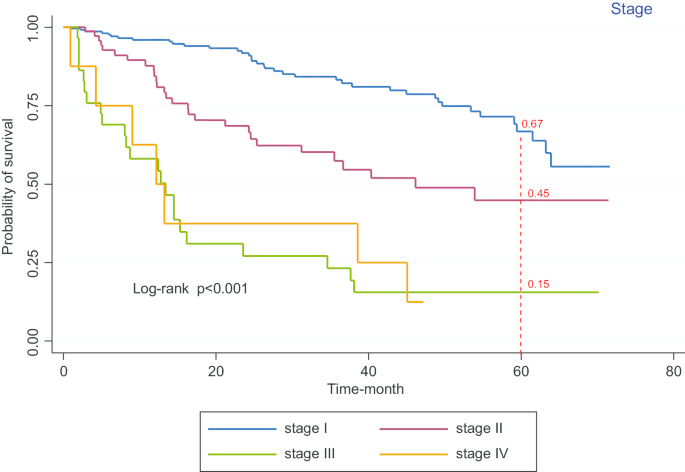
Survival rate of patients with bladder cancer and its related factors in Kurdistan Province (2013–2018): a population-based study | BMC Urology | Full Text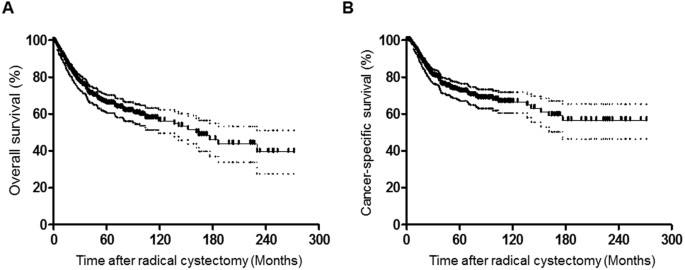
Prognostic factors for conditional survival in patients with muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder treated with radical cystectomy | Scientific Reports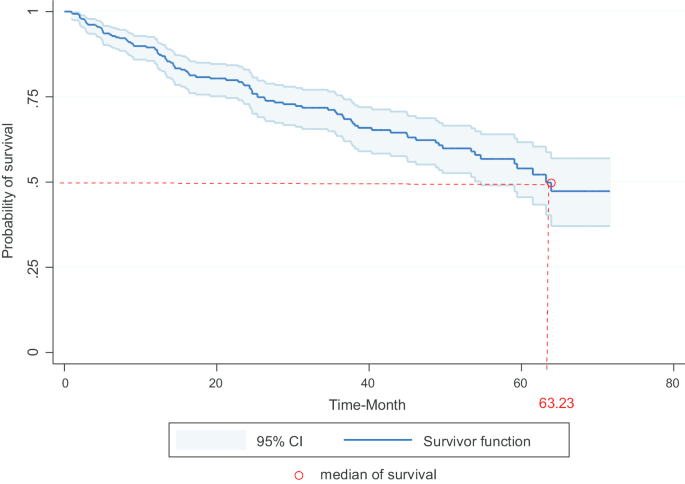
Survival rate of patients with bladder cancer and its related factors in Kurdistan Province (2013–2018): a population-based study | BMC Urology | Full Text
Pathological staging of muscle invasive bladder cancer: is substaging of pT2 tumors really necessary?
Changing cancer survival in China during 2003–15: a pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries - The Lancet Global Health
Prostate cancer survival statistics | Cancer Research UK
Action Bladder Cancer UK
The Team That's Doubling Cancer Survival Rates | Cancer | UT Southwestern Medical Center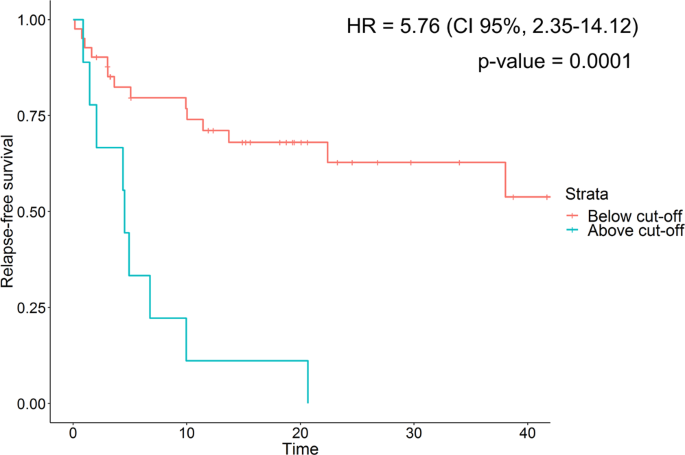
Urinary peptide panel for prognostic assessment of bladder cancer relapse | Scientific Reports
Survival trends in metastatic bladder cancer in the United States: A population based study Shah BK, Mandal R - J Can Res Ther
Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019 - Miller - 2019 - CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians - Wiley Online Library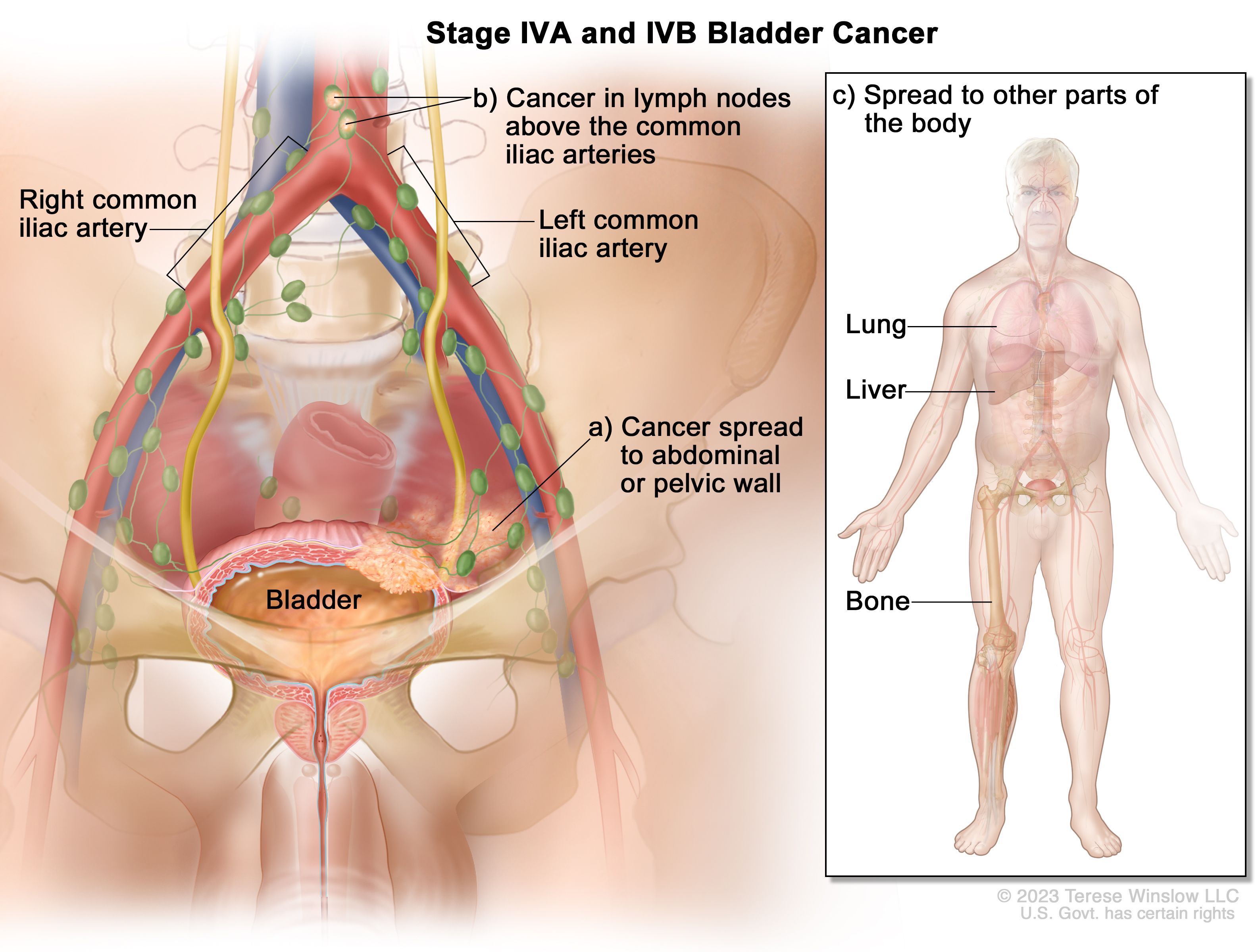
Bladder Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version - National Cancer Institute
Effect of delays in the 2-week-wait cancer referral pathway during the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer survival in the UK: a modelling study - The Lancet Oncology
Stage 4 Bladder Cancer: Prognosis and Life Expectancy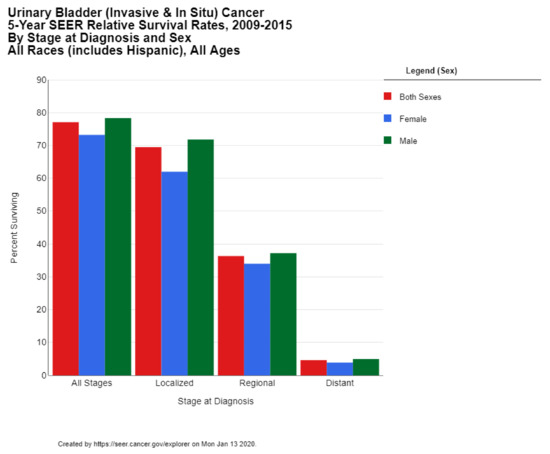
Medical Sciences | Free Full-Text | Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer | HTML
Unfavorable Cancer-specific Survival After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Radical Cystectomy in Patients With Bladder Cancer and Squamous Cell Variant: A Multi-institutional Study - Clinical Genitourinary Cancer
Pembrolizumab as Second-Line Therapy for Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma | NEJM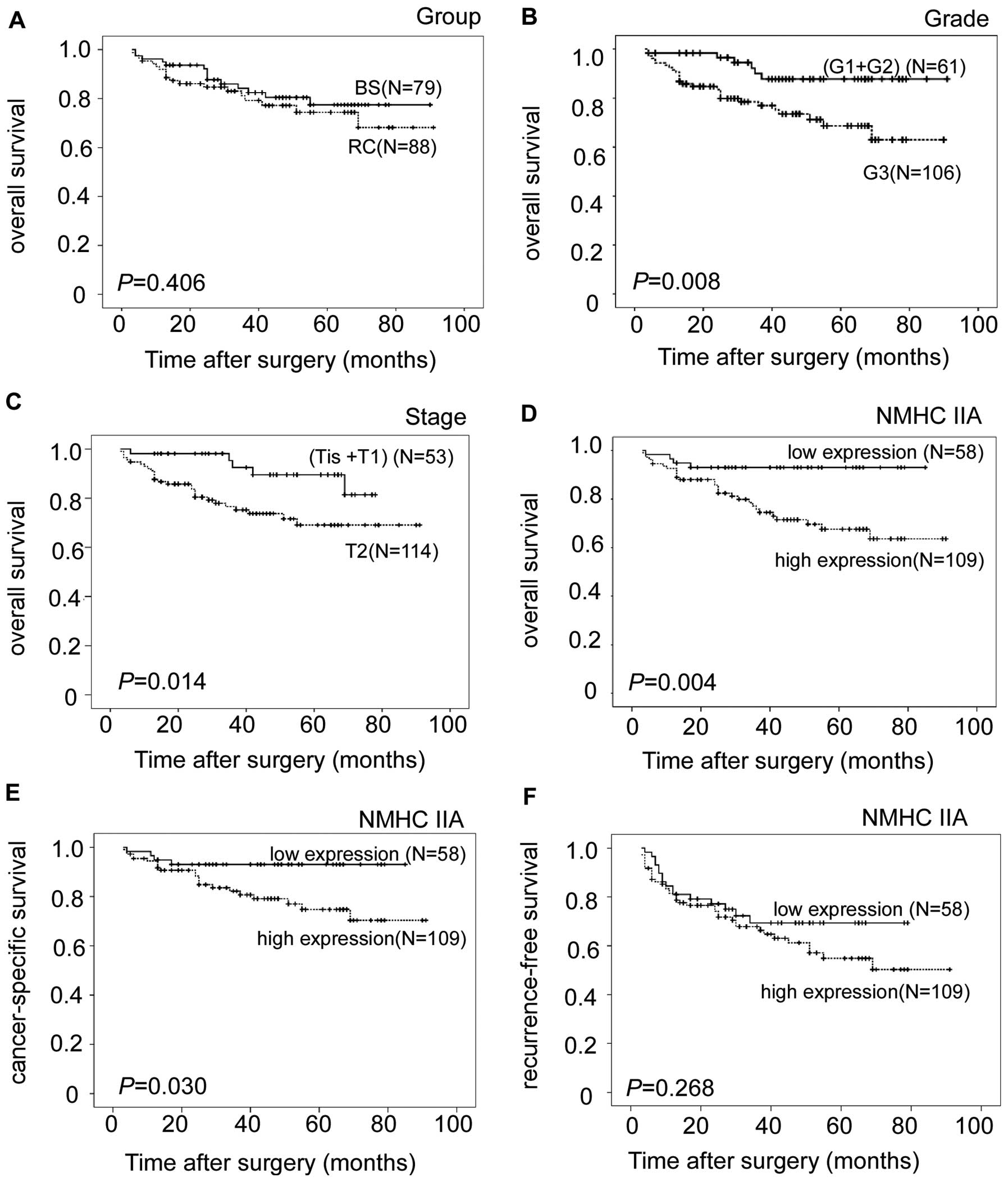
Non-muscle myosin II is an independent predictor of overall survival for cystectomy candidates with early-stage bladder cancer
The potential effect of age on the natural behavior of bladder cancer: Does urothelial cell carcinoma progress differently in various age groups? - ScienceDirect
p53 and ki67 Expression as Prognostic Factors for Cancer-Related Survival in Stage T1 Transitional Cell Bladder Carcinoma - European Urology
MNX1 upregulation is associated with poor prognosis in bladder cancer.... | Download Scientific Diagram
Bladder Cancer Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Bladder Cancer Survival Rate: What to Expect
 Roche - Understanding the impact of bladder cancer
Roche - Understanding the impact of bladder cancer



































Posting Komentar untuk "stage 2 bladder cancer life expectancy"